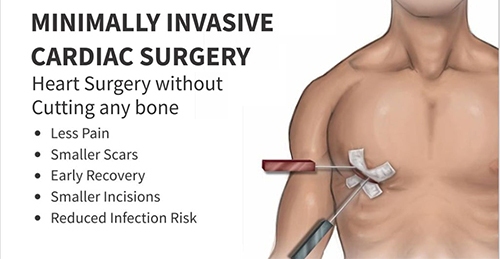
Minimally Invasive Cardiac Surgery
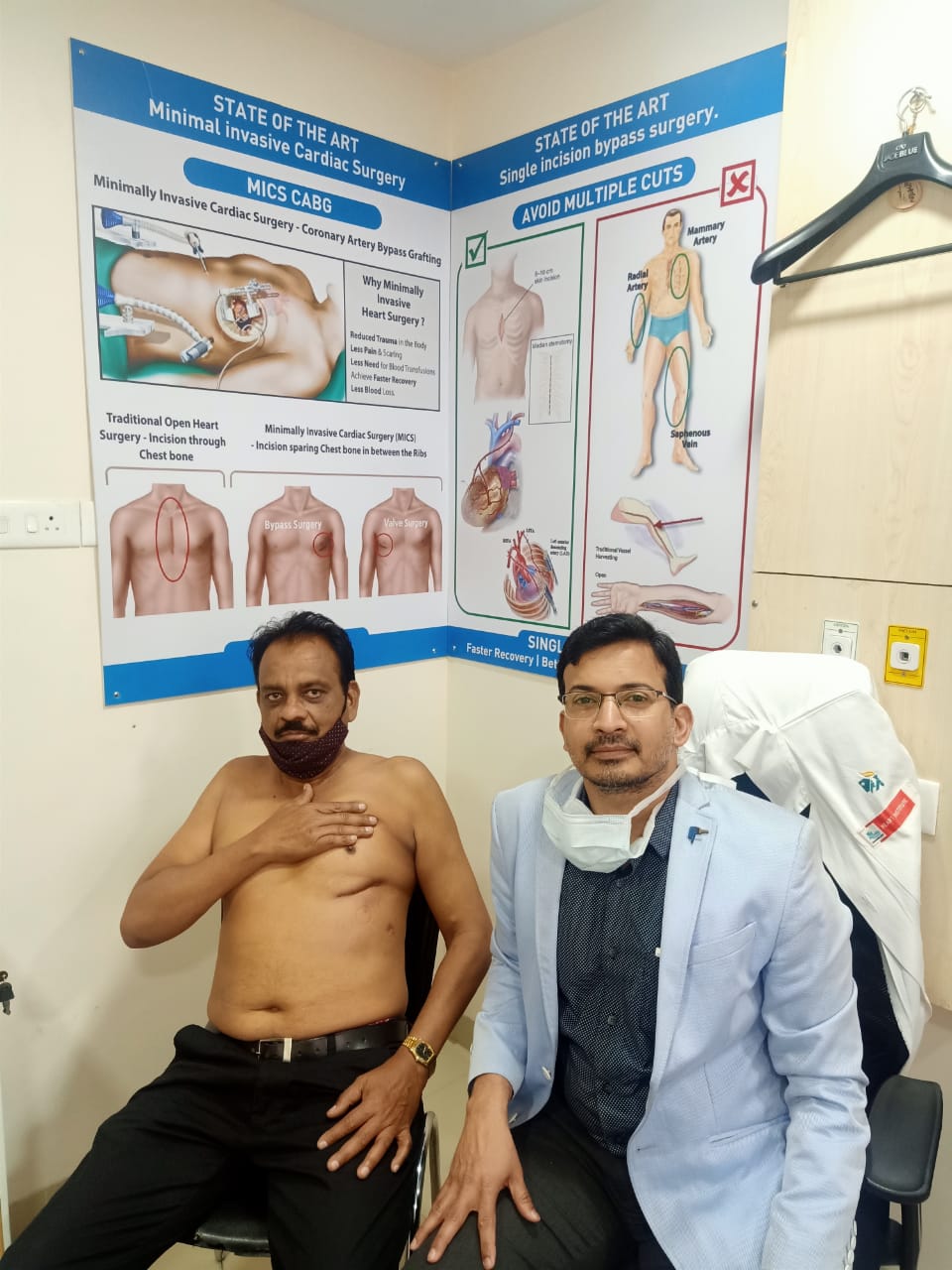
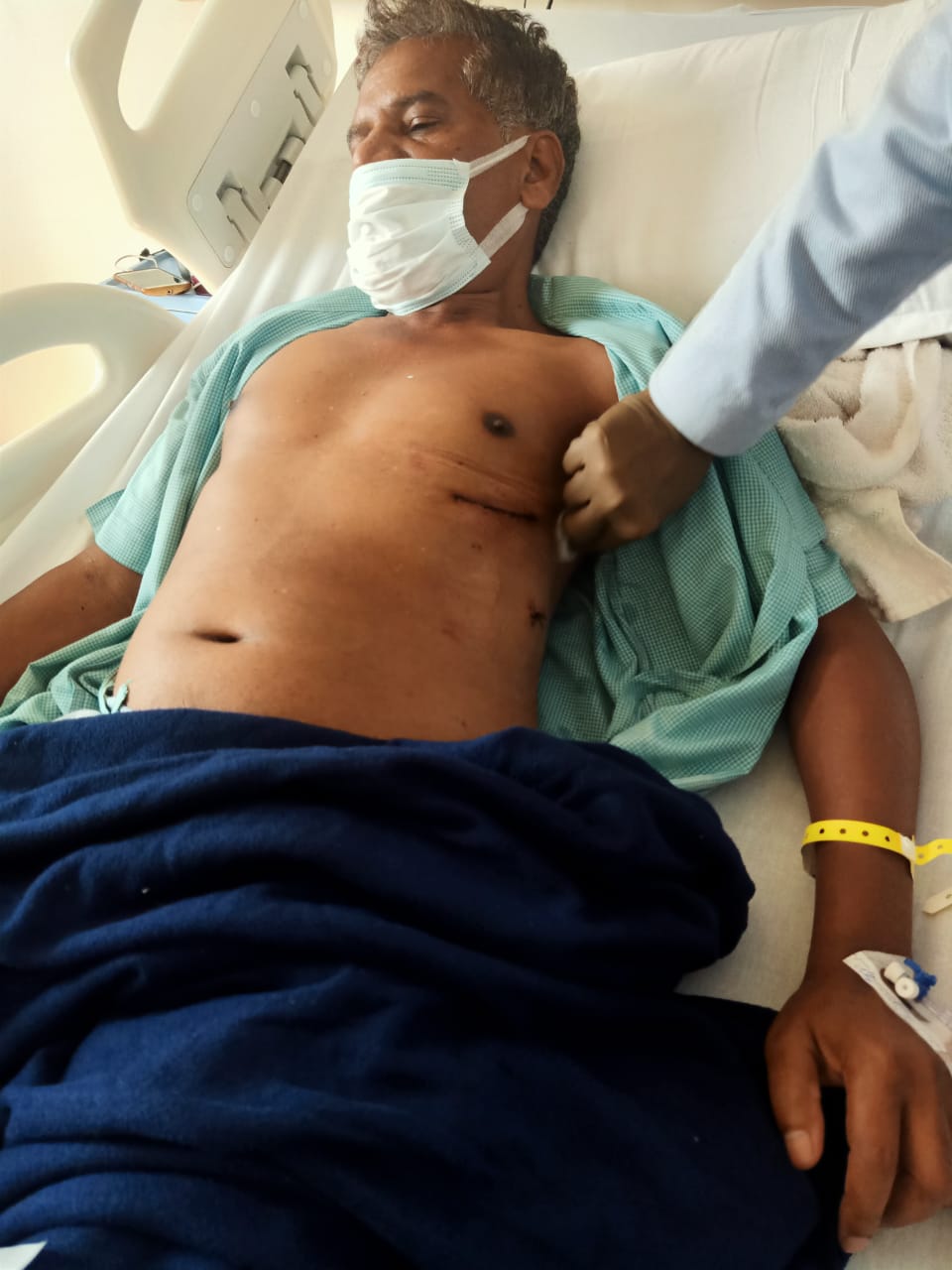
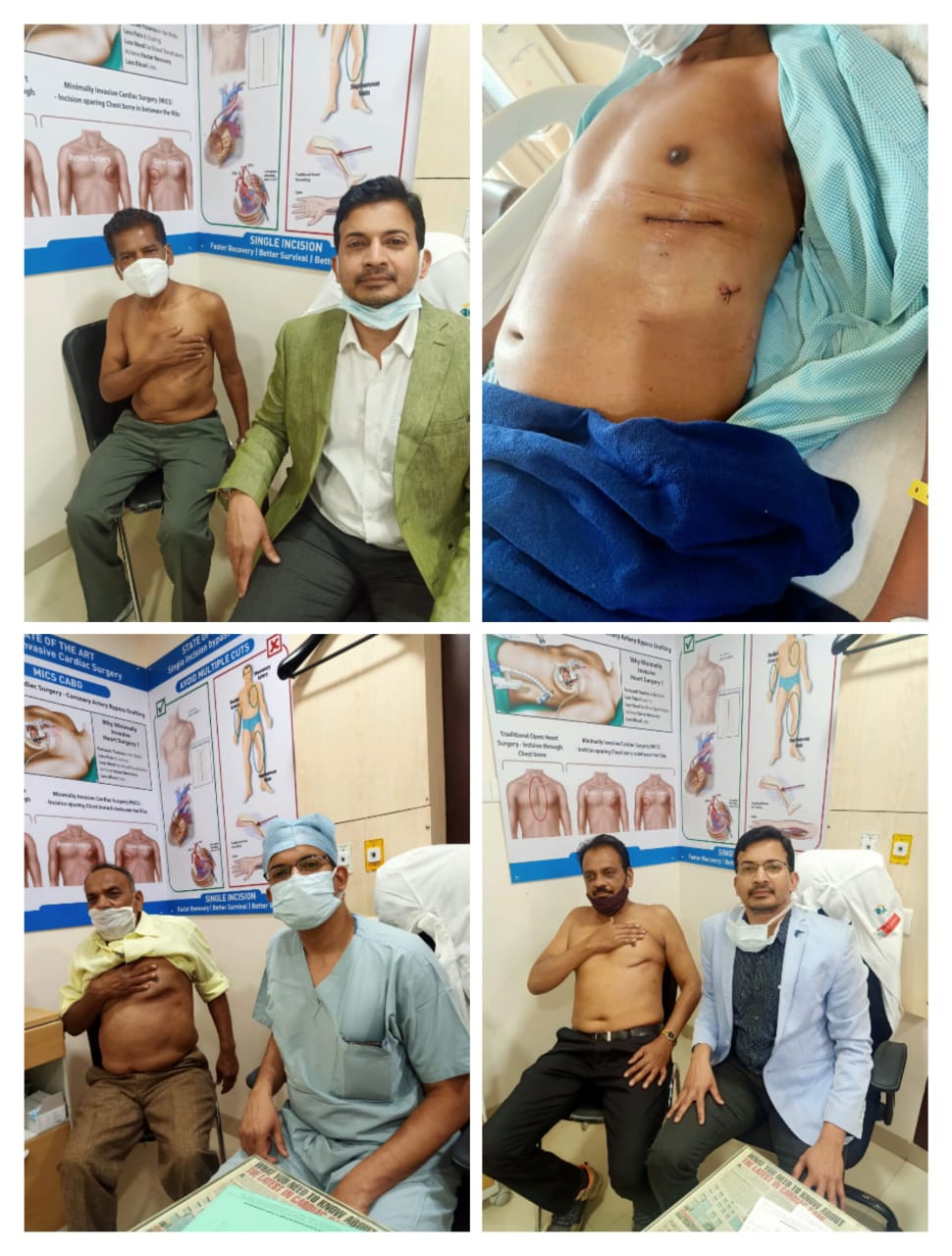
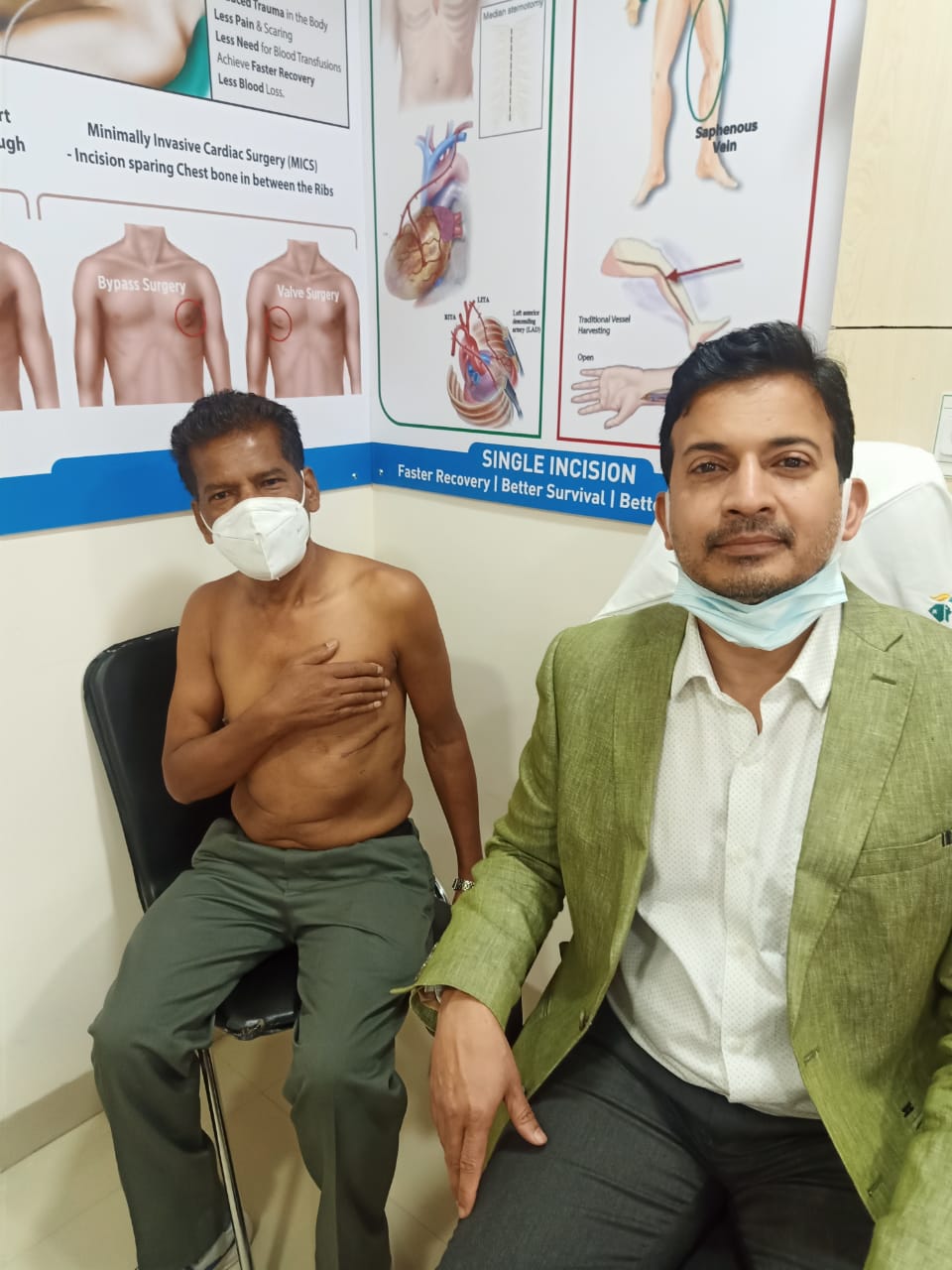
Also known as Key hole surgery , This surgery is less traumatic and leads to early recovery. Instead of cutting breast bone , the heart is approached thorugh right or left chest depending upon the type of surgery
PARTIAL STERNOTOMY – THROUGH PART OF THE BREAST BONE
A 3- to 4-inch long incision is made through the sternum, and the breast bone is separated in that area so the surgeon can see the part of the heart that needs surgery.
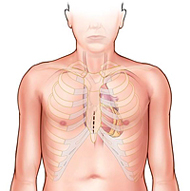
Used for mitral valve, tricuspid valve, epicardial lead placement, atrial septal defect (ASD), patent foramen ovale (PFO), myxoma, and aortic valve surgeries.
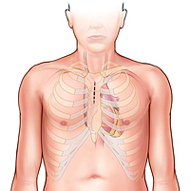
Used for ascending aorta, aortic valve, mitral valve, tricuspid valve, transaortic TAVR, ASD, PFO, myxoma and fibroblastoma surgeries.
MINI-THORACOTOMY
The surgeon avoids cutting through the breastbone and, instead, cuts into muscles between the ribs to reach the heart.
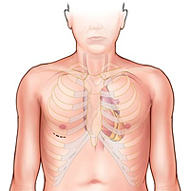
Used for mitral valve, tricuspid valve, ASD, PFO, myxoma surgeries.
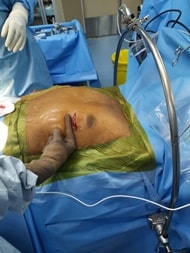
Mini CABG
ADVANTAGES OF MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY
- Increased safety: with a small incision, there's less trauma to the body and far less blood loss.
- Decreased scarring: most incisions just take a stitch or two to close.
- Faster recovery: whereas recovery from traditional surgery typically takes 4-6weeks, patients who have undergone minimally invasive usually takes recovery in only two weeks.
- Decreased length of hospital Stay: 3 to 4 days discharge